Bruker公司开发的捕获离子迁移率谱(trapped ion mobility spectrometry, TIMS)结合高分辨率飞行时间质谱(time-of-flight, TOF)的技术催生了timsTOF系列质谱系统,自2018商品化以来广泛应用于蛋白质组学领域,让这位在核磁谱学领域的“富二代”强势攻入生命科学质谱,成了新领域的“拼一代”。如今,Bruker质谱正以每年更新一款的速度实现快速的产品迭代(笔者注:据网络,用户可以以后期“升级”的方式实现旧换新),并通过频繁的收购(如2020年收购蛋白质组搜索引擎IP2、2022年收购色谱配件PepSep、2023年收购单细胞蛋白质组分析方案PhenomeX)、投资(如2023年实现对泛蛋白质组分析方案Biognosys的主要控股)、合作(如与IonOpticks的OEM合作、与国内几乎所有中大规模的蛋白质组科研服务公司的“战略”合作)等动作,实现其在蛋白质组分析上中下游全领域的渗透。
Bruker质谱能成功,与PASEF方法的建立有果因关系。PASEF全称平行累积-连续碎片化(Parallel Accumulation-Serial Fragmentation),是一种根据tims独特结构而开发的离子迁移和富集技术,可以实现对飞入质谱系统的多肽离子的高效利用,达到了分辨率和灵敏度的双重提高(下图展示了一种初代tims的结构(a)、及其对应的PASEF实现方式(b))。
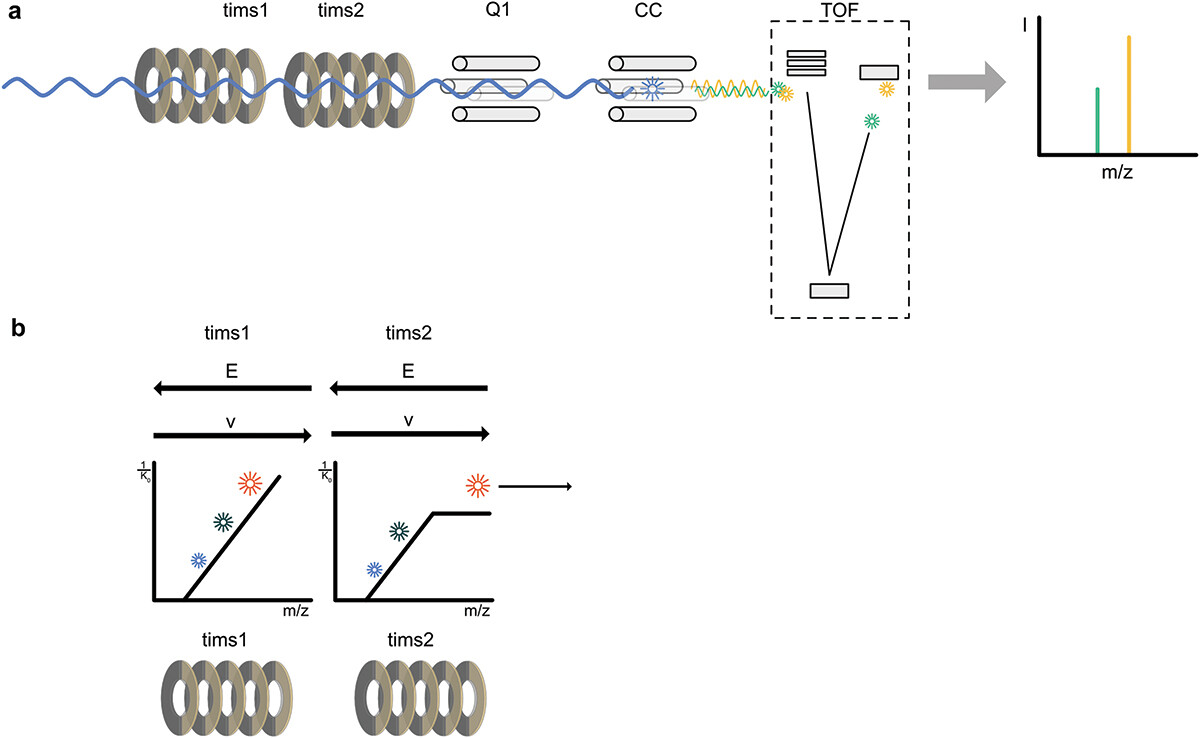
来自卢森堡的研究者们日前在Expert Review of Proteomics上公开了他们关于PASEF方法的综述,汇总了截至投稿(2024年7月)的十一种基于PASEF开发出的质谱采集方法。论文链接:https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14789450.2024.2413092。论文对PASEF的本身技术更迭、对应的质谱方法种类、与重要的应用场景都做了漂亮的介绍,且文字并不冗长,非常推荐读者们赏读并继往开来;笔者在这里不做发挥,仅将11种方法列举于表格(见下表)。为避免与原文不对应,不对表格内容做翻译。
|
PASEF Method |
Applications |
Advantages |
Limitations |
Data Analysis Tools |
|
DDA-PASEF |
Discovery;Quantification at the MS1 level;Spectral library generation |
Data completeness;Stochasticity of the DDA principle |
AlphaTIMS,Mascot,MaxQuant,MS Fragger,ProteoScape,PEAKS XPro,Skyline,SpectroMine | |
|
caps-PASEF |
Cross-linking mass spectrometry |
Reduced selection of mono-linked peptides leads;Increased identification of cross-linked peptides;More effective in preventing the loss of cross-linked peptides in comparison to charge state-based filters |
Non-linked and mono-linked peptides still present;Specialized software needed |
XlinkXFragmentLabMeroX |
|
Thunder-DDA-PASEF |
Immunopeptidomics, specifically small peptides |
Increased likelihood of fragmenting low-abundant peptides;Better separation of co-eluting peptides |
Optimized for HLA-I, but not HLA-II peptides |
MaxQuant,MS Fragger,PEAKS XPro |
|
diaPASEF |
Discovery, Quantifications at the MS2 level |
Overcoming undersampling compared to DDA-PASEF |
Limitations are the same as for DIA |
AlphaTIMS,DIA-NN,MaxQuant,MS Fragger,Mobi-DIK in OpenSWATH,ProteoScape,Skyline,SpectroMine,Spectronaut |
|
Thin-diaPASEF |
Deep proteome profiling |
More sensitive to low-abundant peptides |
Covers a smaller region of precursor ions;Longer cycle time;Decreased throughput |
DIA-NN,ProteoScape,Spectronaut |
|
slice-PASEF |
Discovery, low amounts |
Increased identifications on precursor and protein group level;More precisely quantified peptides;Boosted peptide signals |
Increased cycle time for multiple-frame approaches |
DIA-NN, v 1.8.2 and v 1.9.1 |
|
synchro-PASEF |
Discovery |
Short cycle times;Higher fragment intensities |
Method design needs access for field programmable gate array of the Q1 |
AlphaTIMSDIA-NN, v 1.9.1 |
|
midiaPASEF |
Discovery, generation;Spectral library generation;De novo sequencing |
Increased fragment ion sensitivity;Increased duty cycle;Characteristic MIDIA fingerprints help identifying low-abundant peptides;Increased spectral purity with low interferences or unassigned peaks;Increased mass accuracy and ion statistics;Independent on reconstruction slicing pattern compared to synchro-PASEF |
Method design needs access for field programmable gate array of the Q1 |
MIDIAID pipeline |
|
speedy-PASEF |
Cohort analysis;Routine analysis |
Fast chromatographic methods;High throughput;Decreased sample carry-over between runs;Accelerated column equilibration;Sharper peaks;Higher peak capacity |
High sample amount needed (2000 – 3000 ng) |
DIA-NN |
|
prm-PASEF |
Targeted proteomics |
Removes interferences;Increased sensitivity;Possibility of absolute quantification;Possibility of highly multiplexing the PRM |
Ion mobilities have to be taken into account |
Skyline,Spectrodive |
|
g-dia-PASEF |
Targeted proteomics, Discovery |
Fast measurement;Absolute quantification for selected peptides;Fewer optimization steps need than for prm-PASEF;Higher sensitivity than diaPASEF |
Less sensitive than prm-PASEF |
DIA-NN,Skyline,Spectronaut |